Crystal orientation and insulating ligand of quasi-two dimensional perovskite optimized through silver ion doping for realizing efficient light emitting diodes
In this study, Ag+ doping was performed to control the crystal orientation of Q-2D and realize defect passivation and carrier balance in Q-2D LED devices.
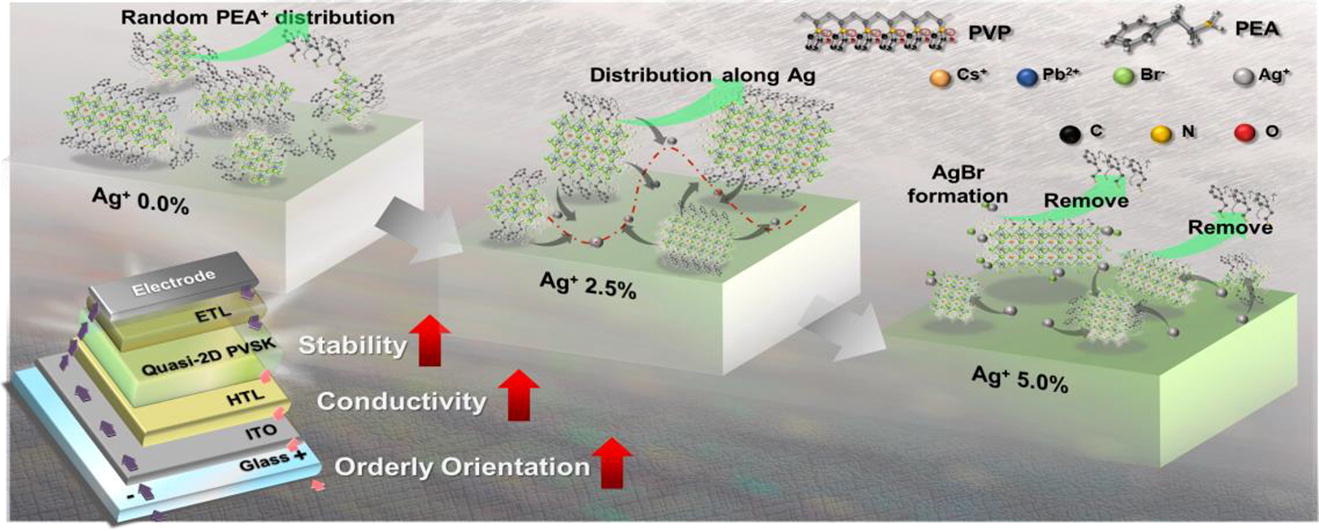
The silver ion (Ag+) doping method has been exploited to improve the disorderly crystal orientation, ligand-insulating properties, and instability properties of quasi-two dimensional perovskite. Furthermore, the superior performance of LED device (high electroluminescence intensity 9507cd cm-2, excellent efficiency, 10.8%) is demonstrated through the appropriate Ag+ doping and modulating effectively the interaction between Pb2+ and phenethylammonium.
Technology Overview
The disorderly orientation crystal in perovskite is inhibited by Ag+ doping. The Ag+ doping performs the defect passivation and carrier balance in LED device. The hole injection barrier is modified by the Ag-nanoparticles-doped process. The optimized device achieves maximum luminance of 9507 cd cm-2 and EQE 10.80%.
Applications & Benefits
Our study breaks new ground in the expansion of ionic strength balance and crystal engineering for realizing efficient Q-2D LED devices.
Abstract:
Quasi-two-dimensional lead halide perovskites (Q-2Ds) have outstanding optoelectronic properties and solution processability, and they have been widely studied as promising candidates for the development of low-cost and efficient LEDs. However, the disorderly crystal orientation and insulating ligand impair the performance of Q-2D-based photoelectronic devices. Thus, a method based on silver (Ag) ion doping is formulated that provides a high dielectric constant, controls the crystal orientation, improves ionic balance, and successfully elevates the LED characteristics of these materials. With the addition of an appropriate amount of Ag+, the disorderly crystal orientation is inhibited, and defect passivation is achieved owing to improvements in photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) and carrier mobility. By contrast, the addition of excess Ag+ increases the possibility of the formation of AgBr during crystal growth, which aggravates the disorderly crystal orientation due to the destruction of ionic balance, which can be attributed to the strong affinity between Ag+ and Br-. Additionally, the hole-transport layer is modified upon Ag nanoparticle doping, which reduces luminescence quenching and hole injection barriers. Consequently, the luminance and external quantum efficiency of the optimized Ag+-doped Q-2D LED are 2 and 10 times higher, respectively, than those of the Q-2D LED without Ag doping.

Crystal orientation and insulating ligand of quasi-two dimensional perovskite optimized through silver ion doping for realizing efficient light emitting diodes
Author:Wei-Cheng Chen, Chung-Wei Hung, Cheng-Hao Chang, Fang-Cheng Liang, Jean-Sebastien Benas, Zhen-Li Yan, Bi-Hsuan Lin, Ja-Hon Lin, Chi-Ching Kuo
Year:2021
Source publication:Chemical Engineering Journal Volume 443, 1 September 2022, 136496
Subfield Highest percentage:99% Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering #3/336
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S138589472201991X
