A novel data-driven optimal chiller loading regulator based on backward modeling approach
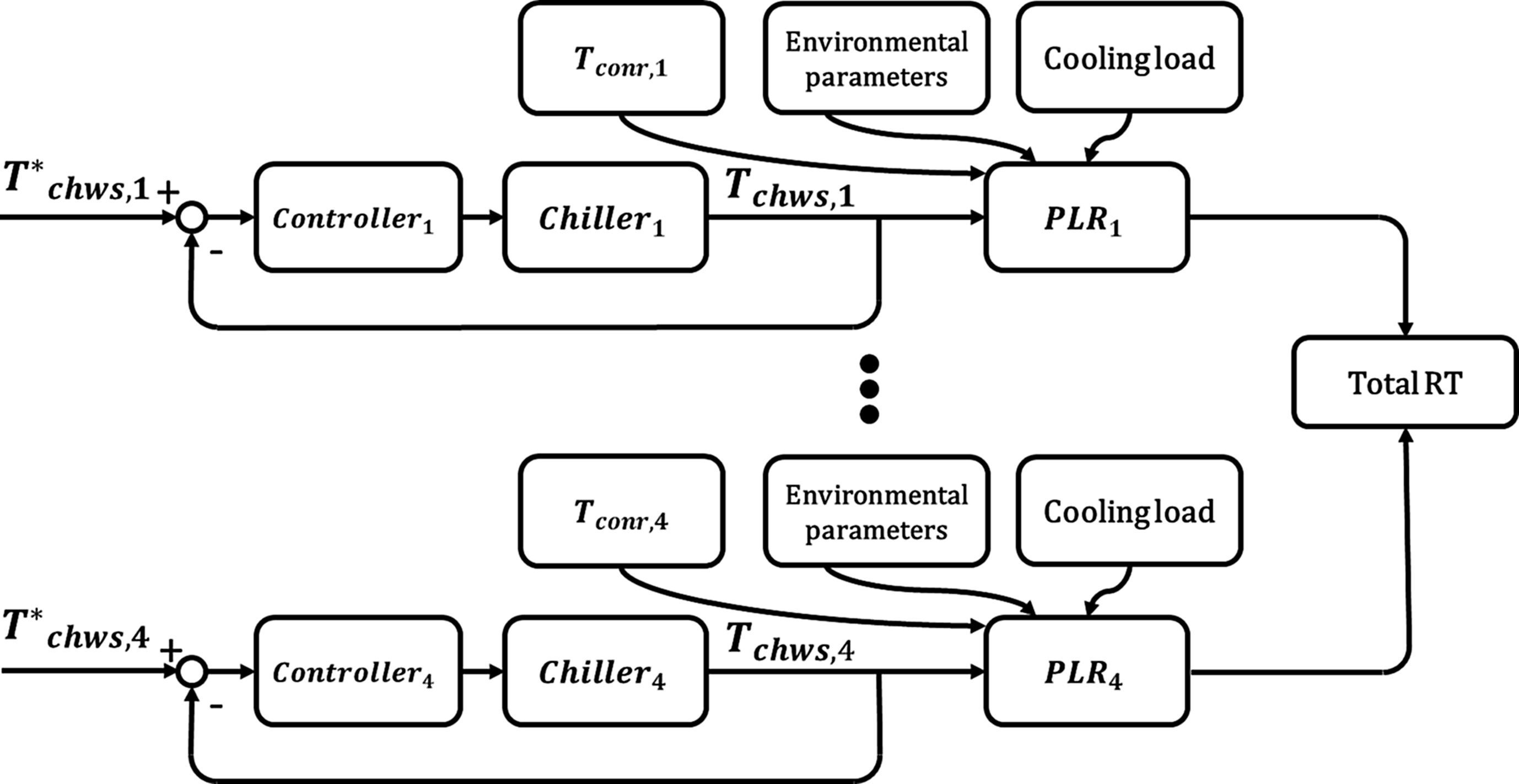
We can illustrate the relationship between Tchws and PLR using the feedback control framework, where the controller built in the chiller will drive the Tchws to track the desired chilled water supply temperature (T*chws). Then, Tchws combining other environmental parameters, condenser water return temperature (Tconr) and cooling load change the value of PLR.
Technology Overview
Developed a novel optimal chiller loading regulator to reduce energy consumption in industries. Deep neural network and conditional generative adversarial network were employed to achieve energy saving. Practical feasibility is verified by conducting 1-year field validation in panel manufacturing factory. Energy can be saved in the range of 81.9 MWh to 198 MWh per year by employing OCLR.
Applications & Benefits
This paper proposes a backward modeling approach (BMA) to achieve practically feasible loading optimization for multiple chillers. This new approach solves the gap between traditional OCL methods and practical realization of these methods. We were able to achieve significant energy saving using the developed OCL regulator (OCLR). Based on the experimental results attained from this work, it is estimated that OCLR can help the factory save about 81.9 MWh to 198 MWh energy per year.
Abstract:
This paper proposes a new method termed backward modeling approach (BMA) to achieve optimal chiller loading (OCL) for reducing energy consumption in industries running multiple-chillers with different efficiency. The developed OCL regulator (OCLR) based on novel BMA approach is composed of conditional generative network (cGAN) and deep neural network (DNN). Most works on the optimal chiller loading problem are to find out the setting of partial load rate (PLR) for each chiller. However, PLR for each chiller cannot be controlled directly and can only be achieved through setting chilled water supply temperature. A novel feedback control framework was developed to identify the relationship between chilled water supply temperature and the PLR. In light of this, the control instruction for chilled water supply temperature can be set to achieve the desired energy saving. The practical feasibility of loading optimization based on developed OCLR was evaluated by conducting field validation for 1 year in a reputed panel manufacturing factory based in Taiwan running multiple-chiller system. From the experimental results, it is evident that the developed data-driven OCLR based on BMA has very high performance and was able to conserve significant energy in the range of 81.9 MWh to 198 MWh per year.

A novel data-driven optimal chiller loading regulator based on backward modeling approach
Author:Kuang-Yow Lian, Yong-Jie Hong, Che-Wei Chang, Yu-Wei Su
Year:2022
Source publication:Applied Energy Volume 327, 1 December 2022, 120102
Subfield Highest percentage:99% Building and Construction #1/211
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261922013599
