Bifunctional Monolayer WSe2/Graphene Self-Stitching Heterojunction Microreactors for Efficient Overall Water Splitting in Neutral Medium
An on-chip platform with a full-cell configuration is needed to study the fundamental mechanism of 2D TMD bifunctional catalysts, where 2D TMD bifunctional catalysts play the role of both the anode and cathode for the HER and OER simultaneously.
Technology Overview
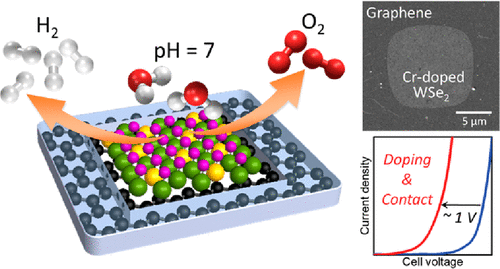
This work demonstrates an on-chip bifunctional WSe2/graphene heterojunction microreactor for efficient overall water splitting in a neutral medium (pH = 7). Through the synergistic atomic growth of the metallic Cr dopant and graphene stitching contact on the 2D ML WSe2, the on-chip bifunctional Cr-doped WSe2/graphene heterojunction microreactors with a full-cell configuration demonstrate an excellent performance for overall water splitting in a neutral medium.
Applications & Benefits
It is found that atomic doping of metallic Cr atoms onto WSe2 can effectively facilitate the charge transfer at the solid–liquid interface. In addition, the direct growth of the graphene stitching contact with the 2D WSe2 catalyst further improves the overall water splitting efficiency of the bifunctional microreactors.
Abstract:
Developing efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts in neutral media to avoid the deterioration of electrodes or catalysts under harsh environments has become the ultimate goal in electrochemical water splitting. This work demonstrates the fabrication of an on-chip bifunctional two-dimensional (2D) monolayer (ML) WSe2/graphene heterojunction microreactor for efficient overall water splitting in a neutral medium (pH = 7). Through the synergistic atomic growth of the metallic Cr dopant and graphene stitching contact on the 2D ML WSe2, the bifunctional WSe2/graphene heterojunction microreactor consisting of a full-cell configuration demonstrates excellent performance for overall water splitting in a neutral medium. Atomic doping of metallic Cr atoms onto the 2D ML WSe2 effectively facilitates the charge transfer at the solid–liquid interface. In addition, the direct growth of the self-stitching graphene contact with the 2D WSe2 catalyst largely reduces the contact resistance of the microreactor and further improves the overall water splitting efficiency. A significant reduction of the overpotential of nearly 1000 mV at 10 mA cm–2 at the Cr-doped WSe2/graphene heterojunction microreactor compared to the ML pristine WSe2 counterpart is achieved. The bifunctional WSe2/graphene self-stitching heterojunction microreactor is an ideal platform to investigate the fundamental mechanism of emerging bifunctional 2D catalysts for overall water splitting in a neutral medium.

Bifunctional Monolayer /Graphene Self-Stitching Heterojunction Microreactors for Efficient Overall Water Splitting in Neutral Medium
Author:Chun-Hao Chiang, Yueh-Chiang Yang, Jia-Wei Lin, Yung-Chang Lin, Po-Tuan Chen, Chung-Li Dong, Hung-Min Lin, Kwun Man Chan, Yu-Ting Kao, Kazu Suenaga, Po-Wen Chiu, and Chun-Wei Chen
Year:2022
Source publication:ACS Nano Volume 16, Issue 11, Pages 18274 - 18283
Subfield Highest percentage:99% General Engineering #1/300
