A novel image protection cryptosystem with only permutation stage: multi-shuffling process
According to the research achievements and valuable experiences from those previous works mentioned above, this paper presents a novel image encryption algorithm with a secure, practical, and sensitive system using an encryption method in data. Said method gives a characteristic of uniqueness in order to handle all information required from the user, such as user account and password to generate the necessary information before running the encryption process.
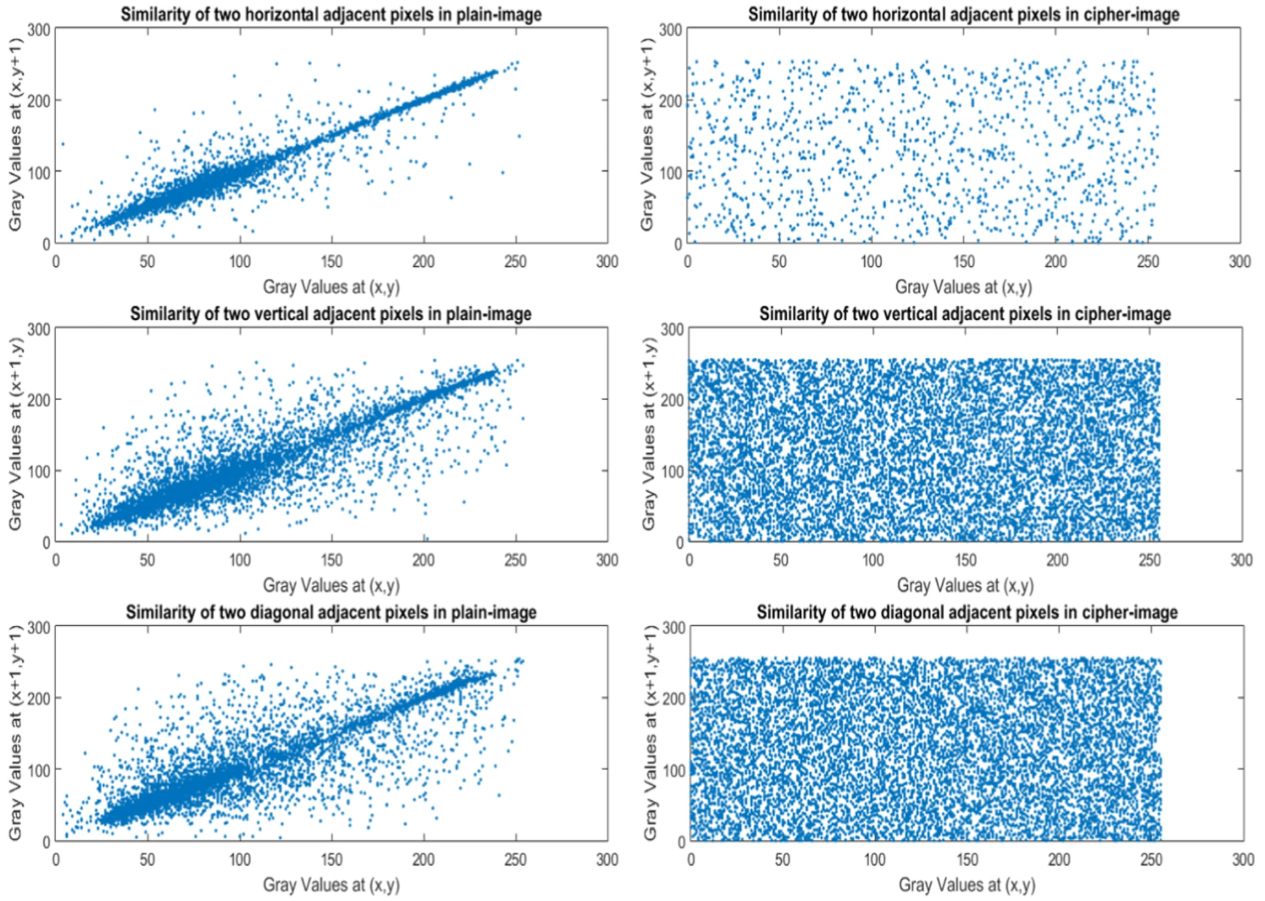
Fig. 13. Correlation of two adjacent pixels
Technology Overview
(1)The flipping procedure is iterated at the beginning of the algorithm; starting to destroy the relationship between adjacent pixels as well as reaching a homogeneous distribution of the number of black/white pixels in the image. (2)A correct and automatic window size at this level; furthermore, the interaction of two chaotic maps that shuffle the position of the selected blocks in pixel level have been designed to help us to relocate and mix all pixels in the image. (3)As a final level, a selected moving window combined with chaotic maps provides the new random position in bit level; this stage allows not only to shuffle the pixels into the selected moving window but also to alter the statistical characteristics of the image modifying the gray values of pixels, reaching an indecipherable image also known as cipher image. Security analysis has been applied to the final result to prove that the proposed image encryption algorithm makes brute-force attacks infeasible.
Applications & Benefits
The proposed method can be useful in communication systems, and even it can be further improved to be implemented in real time. In addition, different hyperchaotic systems can be used instead of using chaotic maps with the purpose of improving the multi-level encryption scheme.
Abstract:
In this paper, a novel cryptosystem with just a multi-shuffling process which is highly interactive to differentiate initial conditions is developed. The proposed system replaces the fundamental and well known in cryptography, confusion–diffusion scheme, which uses two levels with just one confusion block. This algorithm is designed for protecting all personal or commercial data in real-time applications such as monitoring and transmission of multimedia information. The unique confusion stage has three-level shuffling processes, consisting of the flipping procedure, block shuffling, and permutation in a bit level. All of them were designed to drastically change data from a plain image to a cipher image. This not only destroys the relationship of adjacent pixels but also destroys patterns in the encryption process. The flipping procedure tries to combine parts of the image's top with the bottom and the right with the left. The selected columns and rows will change completely after this procedure due to the complement of each pixel being written during the process. The last levels use an automatically sliding window combined with a logistic sine wave and logistic map to drive the iteration of the cryptosystem and shuffle the position of pixels of the plain image as well as giving new statistical features to the image at the same time. The proposed algorithm was designed to be easily implemented by practitioners. Additionally, the main goal of the image encryption is to achieve an uncertain image that cannot be cracked. The results show that this novel cryptosystem with only the shuffling process is well performed and feasible to encrypt images with a high security level. Furthermore, the experimental analysis demonstrates the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed encryption algorithm after being tested using the benchmark “Lena” image, "The Wonder woman" image, and the “Bruce Lee” image, the latter of which is completely different to the first one, statistically speaking.

A novel image protection cryptosystem with only permutation stage: multi-shuffling process
Author:Li Shih-Yu, Miguel Angel Benalcázar Hernández
Year:2023
Source publication:Soft Computing Volume 27 13 March 2023
Subfield Highest percentage:99% Geometry and Topology # 1 / 106
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00500-023-07970-y
