Novel cell screening and prognosing based on neurocomputing-based multiday-ahead time-series forecasting for predictive maintenance of battery modules in frequency regulation-energy storage systems
This research presents a novel battery cell screening and prognosing methodology based on neurocomputing-based multiday-ahead time-series forecasting for predictive maintenance (PdM) of battery modules constituting battery racks of an FR-ESS.
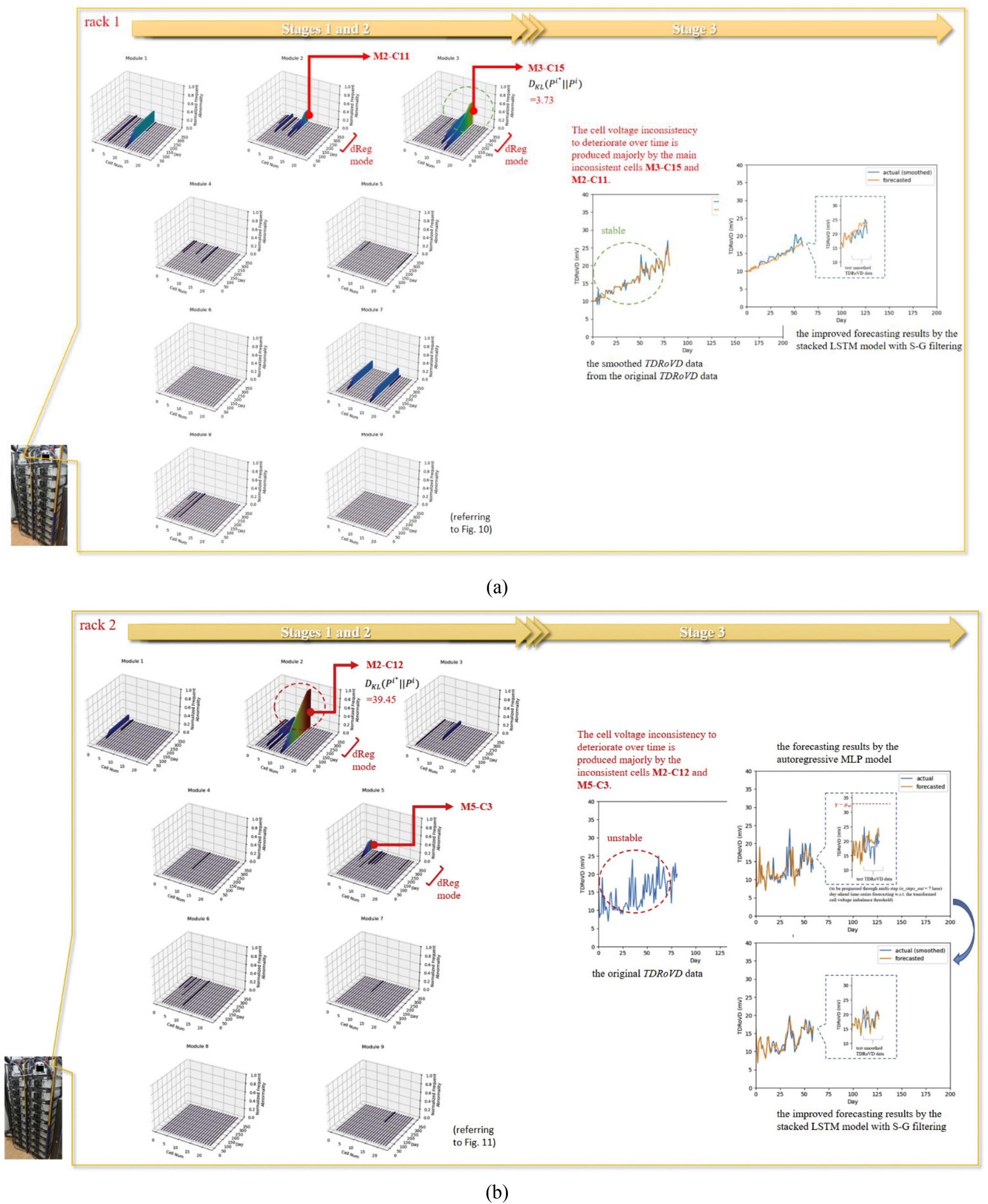
Fig. 30. Illustrative summarization of the developed methodology applied for PdM on the battery system of the investigated FR-ESS where (a) obtained results for rack 1 and (b) obtained results for rack 2 have been summarized and shown.
Technology Overview
An improved battery cell screening process has been proposed. An innovative battery cell prognosing process has also been proposed. The cell prognosing process with the preceding process has been validated really. Experimental results have shown that the processes are feasible and workable.
Applications & Benefits
An improved battery cell screening (diagnosing) process based on fuzzy logic and statistical visualization and analysis (relative entropy) is developed, which can more precisely screen battery cells for their frequent abnormalities related to cell voltage imbalance (i.e., for their frequent abnormalities in cell voltage inconsistency relating to a prespecified battery cell imbalance threshold). Based on battery cell screening results obtained, trended historical cell voltage inconsistency can be modeled by neuro-computing models to be compared in terms of forecasting performance, such that future trend can be predicted for PdM. Finally, the effectiveness of the novel battery cell screening and prognosing methodology is validated on real operational data collected from an actual on-site, in-service FR-ESS.
Abstract:
Energy storage systems (ESSs) by a large number of lithium-ion batteries arranged in series and/or in parallel for their energy storage unit have increasingly become important. This is because, for example, an electrical grid upgraded as a smart grid with a widespread use of renewables and electric vehicles needs to be stabilized under grid requirements for grid safety, stability and reliability. In a frequency regulation (FR)-ESS, (severe) cell voltage imbalance associated with battery performance strongly depending on the aging state and degradation tendency needs to be prevented such that potential safety hazards can be precluded. This research presents a novel battery cell screening and prognosing methodology based on neurocomputing-based multiday-ahead time-series forecasting for predictive maintenance (PdM) of battery modules constituting battery racks of an FR-ESS. Where, battery cell screening can more precisely quantify relative deterioration, relating to cell voltage imbalance, of lithium-ion battery cells, allowing the traceability in terms of cell abnormalities to be quantified and visualized for battery cell outliers inside battery modules. Moreover, from targeted battery cell outliers, battery cell prognosing can predict the tendency of cell voltage inconsistency produced by the main inconsistent battery cells identified from the battery cell outliers so that an alert may be issued and the main inconsistent cells may be considered for maintenance/replacement in PdM. The presented methodology is a preliminary implementation, which has been experimentally validated by an on-site, in-service FR-ESS. Its effectiveness has been confirmed, as reported in this research.

Novel cell screening and prognosing based on neurocomputing-based multiday-ahead time-series forecasting for predictive maintenance of battery modules in frequency regulation-energy storage systems
Author:Lin Yu-Hsiu, Shen Ting-Yu
Year:2023
Source publication:Applied Energy Volume 351, 1 December 2023
Subfield Highest percentage:99% Building and Construction #1 / 223
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030626192301231X
