Versatile deep eutectic solvent assisted synthesis of ZnB2O4 (B = Al, Co, Cr) spinels: The effect of B site variants for comparing the bifunctional electrochemical sensing application
In this work, we discuss the deep eutectic solvent assisted synthesis of ZnB2O4 (B = Al, Co, Cr) electrocatalysts for the simultaneous determination of NF and DM.
Technology Overview
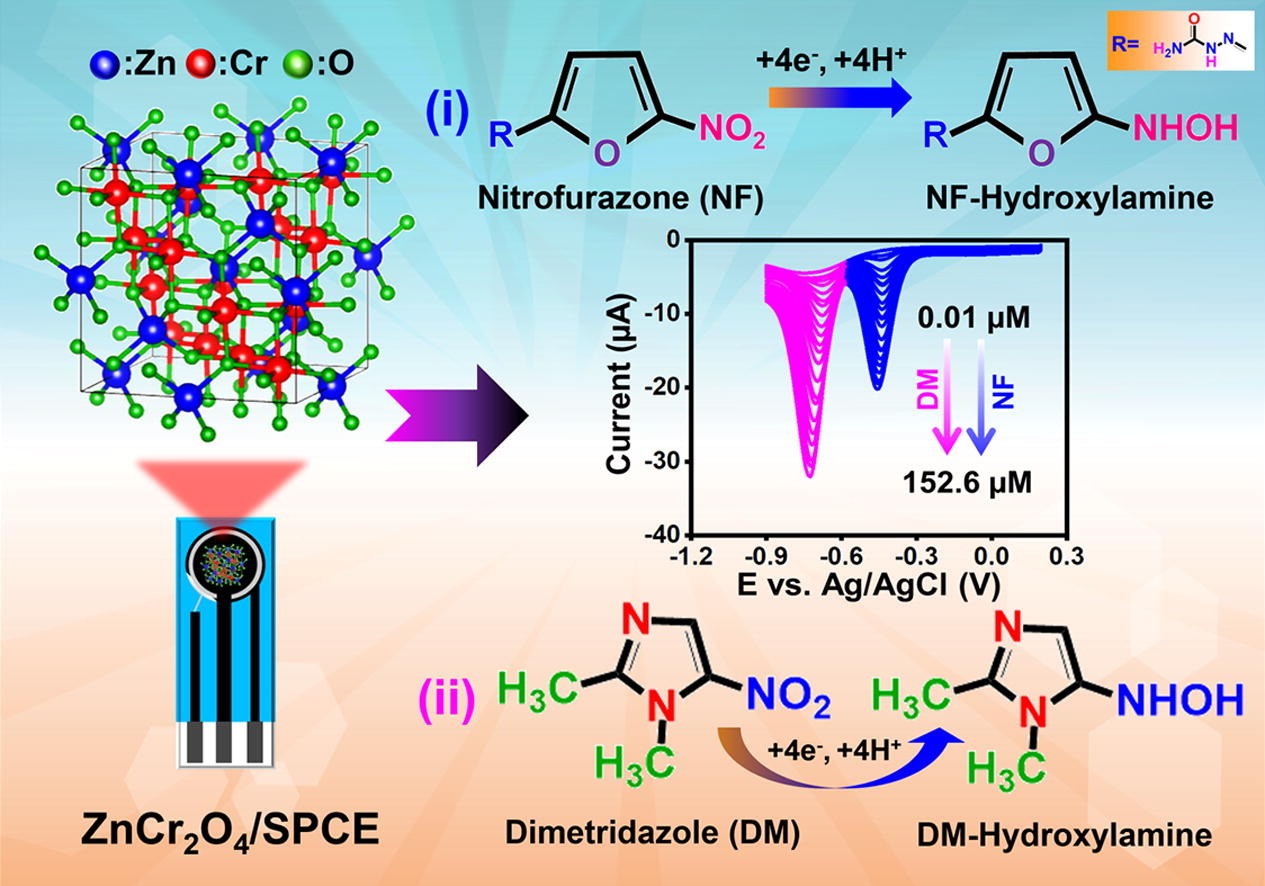
ZnB2O4 (B = Al, Co, Cr) spinels was synthesized by green solvent “deep eutectic solvent method”. ZnB2O4 (B = Al, Co, Cr) were used as electrode materials for nitrofurazone (NF) and dimetridazole (DM) detection. ZnCr2O4/SPCE interface enhanced charge transfer and higher electrocatalytic performance on NF and DM. ZnCr2O4/SPCE exhibited high performance on NF and DM in real samples analysis.
Applications & Benefits
The deep eutectic solvent aided synthesis of the spinels not only circumvents the use of traditional hazardous solvents but also produces atom efficient zinc spinel oxides with its dual solvent-template role. This confirms the sustainable fabrication of sensor materials with reduced energy requisites towards the monitoring of antibiotic residues that helps in assessing the behaviour of pharmaceutical contaminants in the environment.
Abstract:
Antibiotics have been effective in decreasing morbidity and mortality for most of human existence. The wide-spread use and exploitation of antibiotics, on the other hand, has resulted in the evolution of antibiotic resistance, which is now one of the biggest rising threats to global human health. Nitrofurazone (NF) and dimetridazole (DM), two widely used drugs with probable carcinogenicity and mutagenicity, are significant drivers of antimicrobial resistance that can drastically affect the functioning ecosystems. The identification of management options that can reduce the spread of this contamination is thus necessary for limiting its consequences on environmental pathways. In this work, we discuss the deep eutectic solvent assisted synthesis of ZnB2O4 (B = Al, Co, Cr) electrocatalysts for the simultaneous determination of NF and DM. An evaluation on the structural and electrochemical properties of zinc spinel oxides indicate that the B site variants cause element substitution effects that can significantly tune their characteristics. ZnCr2O4 spinel manifests improved simultaneous electrochemical detection of NF and DM which is strongly dependent on its particle size. Also, the proposed sensor establishes desirable features such as linearity, resolution, sensitivity, reproducibility and repeatability which symbols its exploitation in the real-time monitoring of antibiotic pollutants. The deep eutectic solvent aided synthesis of the spinels not only circumvents the use of traditional hazardous solvents but also produces atom efficient zinc spinel oxides with its dual solvent-template role. This confirms the sustainable fabrication of sensor materials with reduced energy requisites towards the monitoring of antibiotic residues that helps in assessing the behaviour of pharmaceutical contaminants in the environment.

Versatile deep eutectic solvent assisted synthesis of ZnB2O4 (B = Al, Co, Cr) spinels: The effect of B site variants for comparing the bifunctional electrochemical sensing application
Author:Jeena N. Baby, Balasubramanian Sriram , Sea-Fue Wang , Mary George
Year:2022
Source publication:Chemical Engineering Journal Volume 435, Part 2 , 1 May 2022, 134136
Subfield Highest percentage:99% Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering #3/336
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894721057090